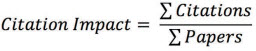% Documents Cited
Percentage of publications cited one or more times.
% Documents in Q1 – Q4
Percentage of documents that appear in a journal in a particular Journal Impact Factor Quartile in a given year. For example, if a value of 10% is displayed, it indicates that 10% of the documents in the set were published in journals of the specified Journal Impact Factor Quartile in that year.
% Documents in Top 1%
Percentage of publications in the top 1% based on citations by category, year, and document type.
% Documents in Top 10%
Percentage of publications in the top 10% based on citations by category, year, and document type.
% Highly Cited Papers
Percentage of publications assigned as highly cited in Essential Science Indicators (ESI) (top 1% by citations for field and year).
% Hot Papers
Percentage of publications assigned as hot papers in ESI (top 0.1% by citations for field and age).
% Industry Collaborations
Percentage of publications that have co-authors from a specific industry.
% International Collaborations
Percentage of publications that have international co-authors.
Academic and Research Staff
The sum total of academic and research staff.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Sum of the number of academic staff and the number of research staff.
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Academic Staff
FTE number of staff employed for an academic post. Excludes clinicians, researchers, and staff no longer active or holding honorary posts.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Academic Staff / Academic and Research Staff
The proportion of all staff academically oriented. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of academic staff by the number of academic and research staff.
Academic Staff / Students – Total
This is sometimes referred to as a “staff-student-ratio” and an indication of the student environment. Its value is a quotient of dividing the number of academic staff by the total number of students.
AcademicSstaff / Undergraduate Degrees Awarded
This is sometimes referred to as a "staff-student-ratio" and an indication of the student environment. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of academic staff by the number of undergraduate degrees awarded.
Academic Staff - International / Academic Staff
The proportion of the academic faculty that are of international origin. This is an indicator of the institution’s ability to attract staff from a global environment.
Affiliation
Researchers affiliated organization.
Article Influence
Determines the average influence of a journal's articles over the first five years after publication. It's calculated by multiplying the Eigenfactor by 0.01 and dividing by the number of articles in the journal, normalized as a fraction of all articles in all publications. This measure is roughly analogous to the 5-Year Journal Impact Factor in that it is a ratio of a journal’s citation influence to the size of the journal’s article contribution over a period of five years.
The equation is as follows: 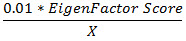 where
X =5-year Journal Article Count divided
by the 5-year Article Count from All Journals.
where
X =5-year Journal Article Count divided
by the 5-year Article Count from All Journals.
The mean Article Influence for each article is 1.00. A score greater than 1.00 indicates that each article in the journal has above-average influence. A score less than 1.00 indicates that each article in the journal has below-average influence.
Average Citations
Mean value or the quotient obtained by dividing the sum total of citations in the dataset by the number of citing articles.
Average Percentile
Average (mean) of the percentiles for all publications.
Baseline
A baseline is the average performance of a global set of publications with the same subject area, document type and year.
Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI)
The CNCI of a set of documents, for example the collected works of an individual, institution or country/region, is the average of the CNCI values for all the documents in the set. It's calculated by dividing the actual count of citing items by the expected citation rate for documents with the same document type, year of publication and subject area. When a document is assigned to more than one subject area an average of ratios of the actual to expected citations is used.
CNCI is a valuable and unbiased indicator of impact irrespective of age, subject focus of document type. A CNCI value of 1 represents performance at par with world average, values above 1 are considered above average and values below 1 are considered below average.
Category Normalized Citation Impact
Citation impact (citations per paper) normalized for subject, year and document type
Category Normalized Citation Impact - Country/Region Adjusted
This is a modification of the category normalized citation impact to take into account the country/region where the institution is based. This reflects the fact that in some regions will have different publication and citation behavior because of factors such as policy, language and size of the research network. The indicator is calculated as the category normalized citation impact of the institution divided by the square root of the category normalized citation impact of the country/region in which it is based.
Citation Impact
The citation impact of a set of documents is calculated by dividing the total number of citations by the total number of publications. Citation impact shows the average number of citations that a document has received.
Citations – Total
Total citations from Web of Science.
Source: Bibliometric Analysis
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Citations – Total / Academic and Research Staff
Citations scaled by the number of the academic and research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of citations by the number of academic and research staff.
Citations – Total / Academic Staff
Citations scaled by the number of the academic staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of citations by the number of academic staff.
Citations – Total / Million Research Income
Cost effectiveness of the research activity as a measure of output (citations) divided by input (funding). Its value is the product of the following formula: (number of citations/research income) * 1,000,000.
Cited Half-life
Median age of the articles that were cited in the JCR year. Half of a journal's cited articles were published more recently than the cited half-life.
Cumulative Probability
Cumulative probability is a statistical method of representing a single value within a normally distributed set of data.
For example, if the value of research income for a given institution is $443,500,650 and its cumulative probability score is 90, then there is a 90% chance that the research income of a randomly selected institution will be less than $443,500,650.
Doctoral Degrees Awarded
The number of advanced research degrees awarded (PhD and equivalent). Includes advanced degrees that include a significant taught component such as a Medical Doctorate, Doctor of Law or Doctor of Engineering and equivalents.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Doctoral Degrees Awarded / Academic Staff
An indication of how successful the institution is at producing doctorates scaled against the number of academic staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of doctoral degrees awarded by the number of academic staff.
Doctoral Degrees Awarded / Doctoral - New Student Intake
The graduation rate is an indicator of the probability that an incoming doctoral student will graduate. Care should be taken to recognize that regional and subject specific trends may influence this indicator.
Doctoral Degrees Awarded / Research Staff
The research staff are used as a scaling measure to show the contrast between doctoral based research and general research. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of doctoral degrees awarded by the number of research staff
Doctoral Degrees Awarded / Undergraduate Degrees Awarded
An indication of which end of the education spectrum upon which the institution is focused. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of doctoral degrees awarded by the number of undergraduate degrees awarded.
Doctoral - New Student Intake
The Full-Time Equivilent (FTE) number of Doctoral (PhD and equivalent) students admitted in this year. These programs are devoted to advanced study and original research and will lead to an advanced research qualification. This will include advanced degrees that include a significant taught component such as a Medical Doctorate , Doctor of Law or Doctor of Engineering and equivalents.
Documents in JIF Journals
Documents published in a journal found in Journal Citation Reports in a given year.
Documents in Q1 – Q4
Number of documents that appear in a journal in a particular Journal Impact Factor Quartile in a given year. For instance, if a value of 100 is displayed, it indicates that 100 documents in the set were published in journals of the specified Journal Impact Factor Quartile in that year.
|
|
InCites uses the best quartile for journals that appear in multiple Web of Science Research Areas. When a research area is specified, the quartile for that particular journal and research area is used. |
Eigenfactor®
The Eigenfactor® calculation is based on the number of times articles from the journal published in the past five years have been cited in the JCR year, but it also considers which journals have contributed these citations so that highly cited journals will influence the network more than lesser cited journals. References from one article in a journal to another article from the same journal are removed, so that Eigenfactors® are not influenced by journal self-citation.
ESI Most Cited
Organizations that are the most cited and therefore included in ESI.
Finances
A set of indicators reflecting the financial performance of the institution.
- Institutional income
- Research income
- Institutional income / students - total
- Institutional income / academic staff
- Research income / academic staff
- Papers / research income
- Research income / papers
5-Year Journal Impact Factor
The average number of times articles from the journal published in the past five years were cited in the JCR year. It's calculated by dividing the number of citations in the JCR year by the total number of articles published in the five previous years
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
A measure of the number of hours worked by an employee considered full-time by an institution. If an institution defines full-time as 40-hours a week, then an employee who works 40 hours/week is 1 FTE. An employee who works 20 hours a week is 0.5 FTE.
Highly Cited Paper
A paper that belongs to the top 1% of papers in a research field published in a specified year. The 1% is determined by the highly cited threshold calculated for the research field in the specified year.
Highly Cited Papers
Papers (articles and reviews) that rank in the top 1% by citations for field and year
H-Index
The h-index is based on a list of publications ranked in descending order by Times Cited. The value of h is equal to the number of papers (N) in the list that have N or more citations.
For example, an h-index of 12 indicates that in the dataset, 12 papers were cited at least 12 times each.
Immediacy Index
The Immediacy Index is the average number of times an article is cited in the year it is published.
- The journal Immediacy Index indicates how quickly articles in a journal are cited.
- The aggregate Immediacy Index indicates how quickly articles in a subject category are cited.
The Immediacy Index is calculated by dividing the number of citations to articles published in a given year by the number of articles published in that year.
Because it is a per-article average, the Immediacy Index tends to discount the advantage of large journals over small ones. However, frequently issued journals may have an advantage because an article published early in the year has a better chance of being cited than one published later in the year. Many publications that publish infrequently or late in the year have low Immediacy Indexes.
For comparing journals specializing in cutting-edge research, the immediacy index can provide a useful perspective.
Impact Relative to World
Citation impact of the set of publications as a ratio of world average.
Institutional Income
The total income of the institution, modified by purchasing power parity (PPP). This will include all forms of income such as general university funds, grant income, contract income, teaching income, donations, investments and commercialization.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Institutional income as reported by the institution, modified by purchasing power parity.
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Institutional Income / Academic Staff
Institutional income scaled against the numbers of academic staff, to give an indication of how well resourced an institution is regardless of its size. It value is the quotient obtained by dividing the institutional income by the number of academic staff.
Institutional Income / Students – Total
The resources available scaled against the number of students. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the institutional income by the total number of students.
Institutional Income / Undergraduate Degrees Awarded
The resources available scaled against the number of students. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the institutional income by the number of undergraduate degrees awarded.
Institutional Performance
A set of indicators reflecting the performance of various non-research characteristics of the institution.
- Teaching reputation - global
- Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Doctoral degrees awarded
- Academic staff / Students - total
- Institutional income / Students - total
- Doctoral degrees awarded / academic staff
- Research staff / academic staff
- Institutional income / academic staff
International Collaboration
Papers that contain one or more international co-authors.
International Diversity
A set of indicators reflecting the international diversity of an institution.
- Academic staff - international / Academic Staff
- Papers with international co-author / Papers - total
- Students - international / Students - total
- Undergraduate - new student intake - international / Undergraduate - new student intake
- Research reputation - international
- Teaching reputation – international
Journal Expected Citations
Average number of citations to articles of the same document type from the same journal in the same database year.
You can compare an article’s citation count to this norm by forming a ratio of actual citations to expected citations--the Journal Actual/Expected Citations ratio. A ratio greater than 1 indicates that the article's citation count is better than average.
For example, the average number of citations received by an article published in 2004 in the journal Circulation is 55.34. This number is the journal expected citations. If an article published in Circulation in 2004 has received 30 citations, the ratio of actual citations to expected citations is .54, indicating a below-average citation count.
On many reports, the Journal Actual/Expected Citations ratio is an aggregate ratio: the denominator (expected citations) is the sum of the expected citations of all journals that the documents were published in. The numerator (actual citations) is the sum of the citation counts of the documents themselves. Division of the sums yields the number shown.
Journal Impact Factor
The Journal Impact Factor is defined as all citations to the journal in the current JCR year to items published in the previous two years, divided by the total number of scholarly items (these comprise articles, reviews, and proceedings papers) published in the journal in the previous two years.
Though not a strict mathematical average, the Journal Impact Factor provides a functional approximation of the mean citation rate per citable item. A Journal Impact Factor of 1.0 means that, on average, the articles published one or two years ago have been cited one time. A Journal Impact Factor of 2.5 means that, on average, the articles published one or two years ago have been cited two and a half times. The citing works may be articles published in the same journal. However, most citing works are from different journals, proceedings, or books indexed in Web of Science.
Journal Impact Factor Quartile
The Journal Impact Factor quartile is the quotient of a journal’s rank in category (X) and the total number of journals in the category (Y), so that (X / Y) = Percentile Rank Z.
| Q1 | 0.0 < Z ≤ 0.25 |
| Q2 | 0.25 < Z ≤ 0.5 |
| Q3 | 0.5 < Z ≤ 0.75 |
| Q4 | 0.75 < Z |
|
|
InCites displays the best quartile for journals that appear in multiple Web of Science Research Areas. When a research area is specified, the quartile for that particular journal and research area is displayed. |
Journal Normalized Citation Impact
Citation impact (citations per paper) normalized for journal, year and document type
Location
Geographic location.
Measures the quotient of an observed citation rate or impact of an institution and an expected citation rate for the institution or country/region. i.e. it compares the performance of an institution to the average performance of the world .
Source: Bibliometric Analysis
Value: Normalized citation impact
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Normalized Indicators
Some indicators include the suffix “normalized." This indicates that the indicator has been modified to overcome differences in subjects. The normalized indicator is calculated as the weighted average of the relative performance in each subject area. This is a three step process:
- The inter-quartile mean of the performance of all institutions is calculated for each subject.
- The performance of the institution in each subject is divided by the inter-quartile mean of the subject. This results in a relative indicator for that subject.
- The weighted average of the institution’s performance across
subjects (Overall) is calculated using the value of the denominator
as the weighting factor.
For example for the indicator “papers / academic staff” the number of academic staff in each subject is used as the weighting factor to calculate the average of the relative indicators.
The normalized indicator for a single subject is the relative indicator as described in step 2.
Organization Type
Type of organization.
Papers / Million Research Income
Cost effectiveness of the research activity as a measure of output (papers) divided by input (funding). Its value is the product of the following formula: (number of papers/research income) * 1,000,000.
Papers – Total
Total papers from Web of Science, limited to articles and reviews.
Source: Bibliometric Analysis
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Papers – Total / Academic and Research Staff
Papers for the institution scaled by the number of academic and research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of papers by the number of academic and research staff.
Papers – Total / Academic Staff
Papers for the institution scaled by the number of academic staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of papers by the number of academic staff.
Papers with International Co-author / Papers – Total
The proportion of the papers authored by the institution that contain a co-author from a country/region other than the country/region in which the institution is based. This is an indicator of the institution’s ability to collaborate in a global environment.
Percentile in Subject Area
The percentile in which the paper ranks in its category, document type and database year, based on total citations received by the paper. The higher the number of citations, the larger the percentile number. The top ranked documents will have the highest percentile. Documents in the top 10% will be in the 90–100th percentiles. Documents with a percentile of 99 will be ranked higher than the other 99%.
In the document list view, subject areas are sorted by the corresponding paper's performance in that subject area, so that the first listed subject area corresponds to the percentile in subject area indicator.
Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) adjusts the exchange rate between currencies by taking into account the actual cost to purchase the same goods in the home countries of the currencies. InCites uses Purchasing Power Parity data from the International Monetary Fund’s World Economic Outlook Database (Surveys 2010) to convert the value of monetary indicators such as research income into U.S. dollars.
Rank
Rank order in the list of results
Reputational Characteristics
A set of indicators reflecting the reputational standing of the institution and performance relating to reputation.
- Teaching reputation - global
- Research reputation - global
- Normalized citation impact
- Research income / academic staff
- Research power / research income
- Citations / academic staff
Reputation – Research (Group)
The reputational standing, for research, of an institution in various geographical regions.
- North America
- Latin America
- Africa
- Asia
- Europe
- Oceania
Reputation – Teaching (Group)
The reputational standing, for teaching, of an institution in various geographical regions.
- North America
- Latin America
- Africa
- Asia
- Europe
- Oceania
Research Capacity and Performance
A set of indicators associated with research performance.
- Academic and research staff
- Research income
- Papers - total / Academic and research staff
- Papers - total / Million research income
- Research income / Academic and research staff
- Research reputation - global
Researcher ID
ID associated with a researcher.
Research Income
The amount of income that the institution has acquired specifically for research.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Research income as reported by the institution, modified by purchasing power parity.
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Research Income / Academic and Research Staff
Research income scaled against academic staff and research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by the number of academic and research staff.
Research Income / Academic Staff
Research income scaled against the academic staff, to give an indication of how well resourced an institution is regardless of its size. It is also an indication of the academic staff’s ability to attract research funding. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by the number of academic staff.
Research Income / Citations – Total
The research income scaled by the number of citations. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by the number of citations.
Research Income / Institutional Income
How intensively an institution is focused on research. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by institutional income.
Research Income / Papers – Total
The research income scaled by the number of papers. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by the number of papers.
Research Income / Research Staff
Research income scaled against the number of research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income by the number of research staff.
Research Income from Industry
This is the amount of research income acquired from industry or other commercial entities.
Research Income from Industry / Academic and Research Staff
Research income from industry scaled against the number of academic and research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income from industry by the number of academic and research staff.
Research Income from Industry / Academic Staff
Research income from industry scaled against the number of academic staff to give an indication of how successful an institution is at acquiring income from industry regardless of its size. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income from industry by the number of academic staff.
Research Income from Industry / Research Income
How intensively research is funded be industry. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income from industry by research income.
Research Income from Industry / Research Staff
Research income from industry scaled against the number of research staff. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing research income from industry by the number of research staff.
Research Output
A set of indicators representing the research output of an institution.
- Citations - total
- Papers - total
- Research income
- Papers - total / Academic staff
- Papers - total / Million research income
- Doctoral degrees awarded / Academic staff
- Research reputation - global
Research Performance
A set of indicators associated with research performance.
- Normalized citation impact
- Papers - total / Academic Staff
- Doctoral degrees awarded / Academic Staff
- Research income / Academic Staff
- Research income / Institutional income
- Research reputation - global
Research Power
The research power of the institutions as measured by the normalized citation impact multiplied by the number of academic staff. It is a value equivalent to the total number of citations normalized for the subject and year.
Source: Bibliometric Analysis
Value: Multiple of normalized citation impact and number of academic staff
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Research Power / Million Research Income
Indication of the volume and citedness of research scaled by the research income. Its value is the product of the following formula: (research power/research income) * 1,000,000.
Research Reputation – Global
Results of the Academic reputation survey for research.
Source: Academic Reputation Survey
Value: Average of values weighted according to country/region of respondent. Values can range from 0-100.
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Research Reputation – Global
Results of the Academic reputation survey for research limited to geographical regions other than the one in which the institution is based.
Source: Academic Reputation Survey
Value: Percentage of the responses that selected this institution
Score: Exponentially scaled Cumulative Probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100
Research Size
A set of volume related indicators of research performance.
- Citations - total
- Papers - total
- Doctoral degrees awarded
- Research staff
- Research income
- Research power / Million research income
Research Staff
FTE number of people who are employed only to perform research, excluding academic staff.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Research Staff / Academic and Research staff
The proportion of all staff focused on research. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of research staff by the number of academic and research staff.
Research Staff / Academic staff
How intensively an institution is focused on laboratory research. Its value is the quotient obtained by dividing the number of research staff by the number of academic staff.
Scaled Characteristics
A set of indicators reflecting various size independent characteristics of the institution.
- Normalized citation impact
- Academic Staff / Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Academic Staff / Students - total
- Papers - total / Million research income
- Research reputation - global
- Teaching reputation - global
Score
A number from 1-100 that represents the probability that any value randomly selected will fall below the value represented by that number. The score is calculated by cumulative probability.
A score places a value in context and allows for meaningful comparisons. For example, if the number of academic staff for an institution is 300, it is impossible to judge whether that is a large or small number in relation to other institutions. If the indicator (academic staff) receives a score of 50, then it is reasonable to conclude that 300 is average; that is, there is a 50% probability that the size of the academic staff of another institution randomly selected will be smaller than 300.
Sheer Size
A set of indicators that measure the overall size of the institution.
- Academic staff
- Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Institutional income
- Papers - total
- Doctoral degrees awarded
- Research staff
- Research power
- Students - total
Students – international / Students – total
The proportion of students that are of international origin. This is an indicator of the institution’s ability to attract students from a global environment. Care should be taken to recognize that regional and subject specific trends may influence this indicator.
Students – total
This is the FTE number of students of all programs that lead to a degree, certificate, institutional credit or other qualification. It will include students of all years of study. Typically these will be undergraduate and postgraduate students who are studying for Higher Education programs such as Bachelors, Masters or Doctoral or other equivalent degrees or components of those programs.
Subject area count
The number of total subject areas for the documents attributed to the funding agency in the dataset.
Teaching performance
A set of indicators reflecting the teaching performance of an institution.
- Academic Staff / Students - total
- Undergraduate degrees awarded / Undergraduate - new student intakeScaled Characteristics
-
A set of indicators reflecting various size independent characteristics of the institution.
-
- Normalized citation impact
- Academic Staff / Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Academic Staff / Students - total
- Papers - total / Million research income
- Research reputation - global
- Teaching reputation - global
-
Score
-
A number from 1-100 that represents the probability that any value randomly selected will fall below the value represented by that number. The score is calculated by cumulative probability.
-
A score places a value in context and allows for meaningful comparisons. For example, if the number of academic staff for an institution is 300, it is impossible to judge whether that is a large or small number in relation to other institutions. If the indicator (academic staff) receives a score of 50, then it is reasonable to conclude that 300 is average; that is, there is a 50% probability that the size of the academic staff of another institution randomly selected will be smaller than 300.
-
Sheer Size
-
A set of indicators that measure the overall size of the institution.
-
- Academic staff
- Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Institutional income
- Papers - total
- Doctoral degrees awarded
- Research staff
- Research power
- Students - total
-
Students – international / Students – total
-
The proportion of students that are of international origin. This is an indicator of the institution’s ability to attract students from a global environment. Care should be taken to recognize that regional and subject specific trends may influence this indicator.
-
Students – total
-
This is the FTE number of students of all programs that lead to a degree, certificate, institutional credit or other qualification. It will include students of all years of study. Typically these will be undergraduate and postgraduate students who are studying for Higher Education programs such as Bachelors, Masters or Doctoral or other equivalent degrees or components of those programs.
-
Subject area count
-
The number of total subject areas for the documents attributed to the funding agency in the dataset.
- Doctoral degrees awarded / Academic Staff
- Doctoral degrees awarded / Undergraduate degrees awarded
- Doctoral degrees awarded / Doctoral - new student intake
- Students - international / Students - total
- Teaching reputation - global
Teaching reputation – global
Results of the Academic reputation survey for teaching.
Source: Academic Reputation Survey
Value: Average of values weighted according to country/region of respondent. Values can range from 0-100.
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Teaching reputation – international
Results of the Academic reputation survey for teaching limited to geographical regions other than the one in which the institution is based.
Source: Academic Reputation Survey
Value: Percentage of the responses that selected this institution
Score: Exponentially scaled Cumulative Probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100
THE Ranked
A ranking of universities published by Times Higher Education and based on citation database information from Clarivate Analytics (top 400).
Times Cited
Number of times the set of publications has been cited
Undergraduate Degrees Awarded
The number of degrees awarded for a taught program that is the first significant stage of the institution’s academic program. In many countries this is termed a “bachelor” degree.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Raw number
Score: Cumulative probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100.
Undergraduate Degrees Awarded / Undergraduate - New Student Intake
The graduation rate is an indicator of the probability that an incoming undergraduate student will graduate. Care should be taken to recognize that regional and subject specific trends may influence this indicator.
Undergraduate - New Student Intake
This is the FTE number of students entering the institution, or this level of education, for the first time during this year for a taught program that is the first significant stage of your institution’s academic program. This is often known as a Bachelor’s student.
Source: Institutional Data Collection
Value: Raw Number
Score: Cumulative Probability score of the value. Scores can range from 1-100
Undergraduate – New Student Intake – International / Undergraduate – New Student Intake
The proportion of undergraduate students that are of international origin. This is an indicator of the institution’s ability to attract students from a global environment. Care should be taken to recognize that regional and subject specific trends may influence this indicator.
Web of Science Documents
The number of Web of Science documents.